自動運転 - 自己位置推定
Autonomous Driving - Self-Localization
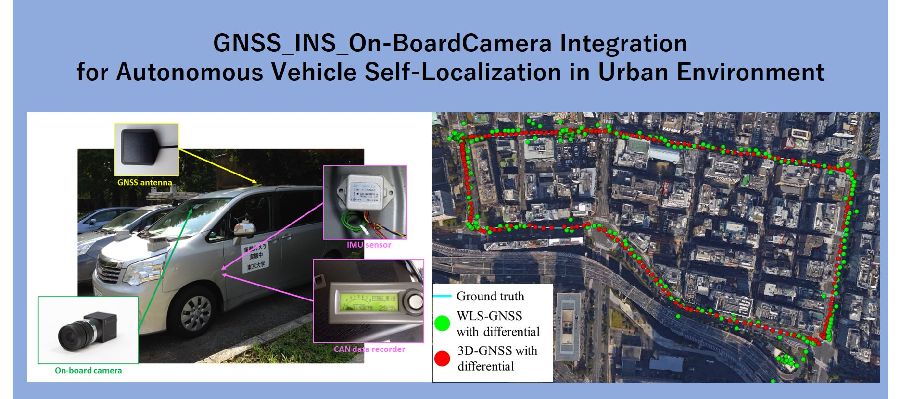
近年、注目を集める運転支援システムや自動運転システムにおいて、自車両の位置推定は不可欠な技術です。 しかし、人工衛星からの信号の遮蔽・反射が起こる都市部においては、Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS)による測位は高い精度を保てません。 一方で、Inertial Navigation System (INS)は短時間の相対的な移動を正確に推定できるますが、誤差の蓄積により時間とともに精度は悪化していきます。 そこで本研究は、従来のGNSSおよびINSの測位システムに加えて、2次元地図と車線検出を統合した測位手法を提案しました。 これにより自車両が走行している車線の特定が可能となることが期待されます。また、複数のセンサ情報の統合にはバーティクルフィルターを用いています。 INSは速度計とInertial Measurement Unit (IMU)からなり、これらの進行速度・方向を通して得られる車両のモーションを用いて、パーティクルを伝搬させます。 そして、GNSSはグローバルな座標系における測位結果を返し、パーティクルごとの尤度を与えます。 車線検出は車両の中心から左右それぞれの白線までの距離を認識し、これによりさらに尤度の高いパーティクルを決定します。 都市部環境下における実験結果において、これらの統合測位システムは1m以下の測位精度を持ち、走行車線の認識率が95%であることを示しました。
Vehicle self-localization is an important and challenging issue in current driving assistance and autonomous driving research activities. The occupied lane identification enables more precise guiding along the desired trajectory and vehicle cooperation, such as lane changing. The land vehicle navigation system typically has to operate in the areas where Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) signal is either blocked or reflected, such as unban canyon. Inertial Navigation System (INS) can provide accurately relative vehicle position in short time, but its accuracy degrades with time because of accumulated error. This research proposes to integrate 2D map and vision-based lane detection with GNSS/INS positioning system, which is expected to determine the occupied lane of the host vehicle. We proposes to use the particle filter for multiple cue integration. INS is consist of speedometers and Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU), which can describe motion of vehicle via velocity and heading direction. The motion of the vehicle is used for particle propagation in the integration algorithm. GNSS gives global localization measurement, which can estimate probability of particles. Lane detection percepts the relative distance from the center of vehicle to left white line and right white line. This distance is an additional measurement to refine the probability of particles. Finally, the developed system was tested in an urban environment. The experimental result demonstrated that integration of GNSS/INS/lane detection can achieve sub-meter accuracy and more than 95% correct lane rate.