自動運転にとって悪環境におけるセンシング状況を把握することはとても重要です。当研究室ではこのテーマに対して、悪環境に対するセンシングをシミュレートするデータ生成などの研究を行っています。
For automated driving, it is very important to understand sensing conditions in adverse environments. In our laboratory, we are conducting research on this theme, including data generation to simulate sensing in adverse environments.
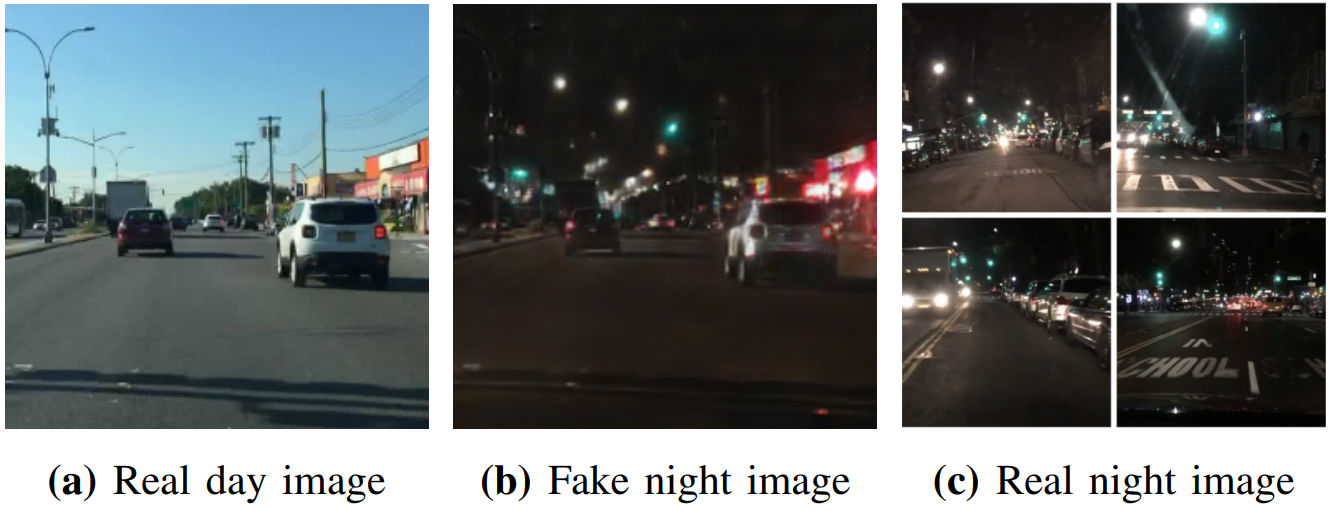
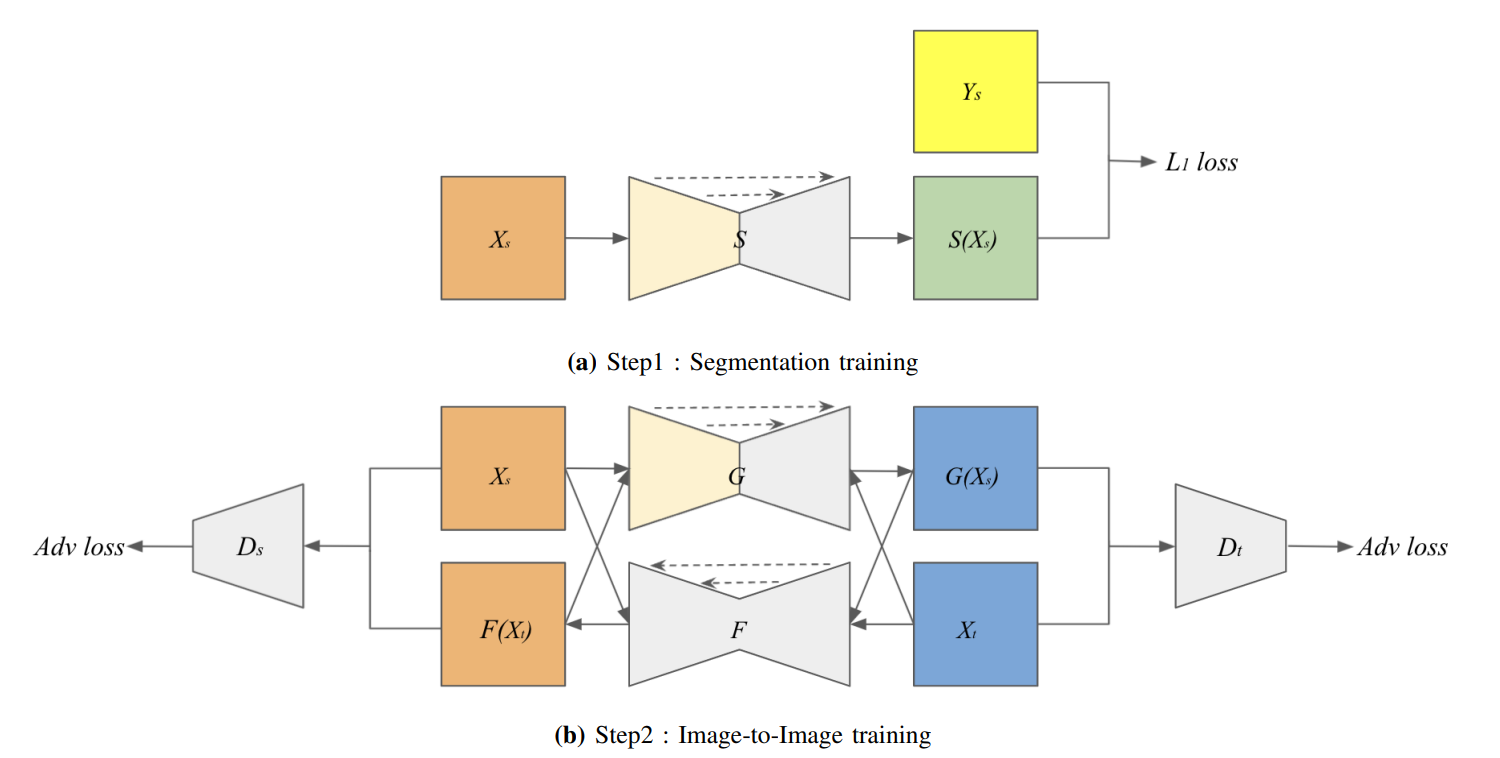
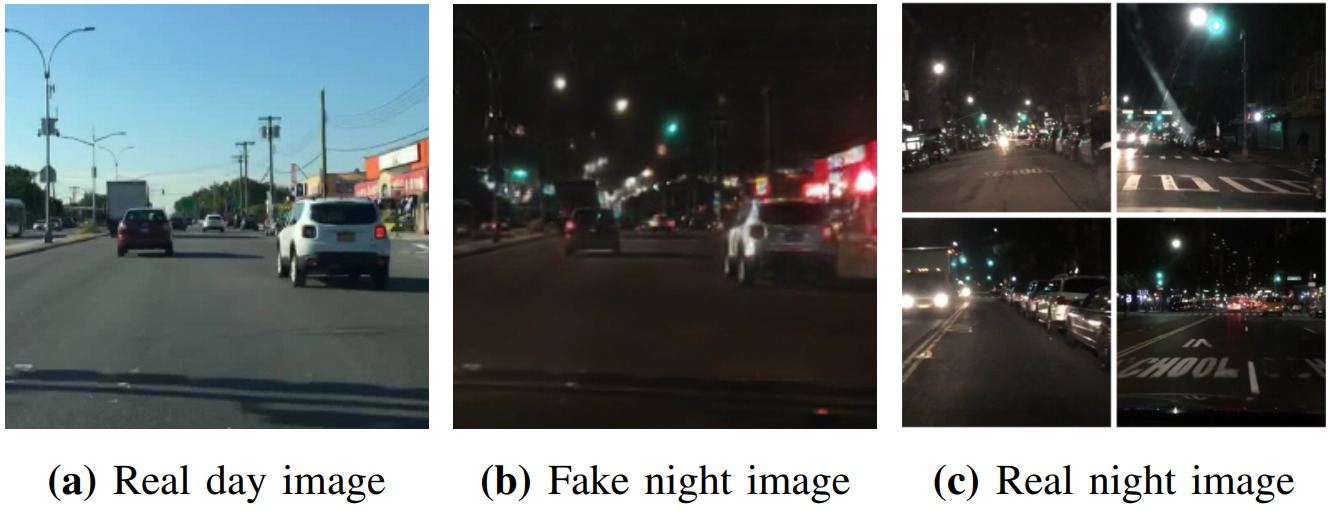
昼間の交通画像を夜間の画像へ変換するために、Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) による画像生成とSemantic Segmentationを組み合わせたモデルを提案します。
We proposed a generative model to use semantic segmentation networks in GANs for the day-to-night image style transfer.
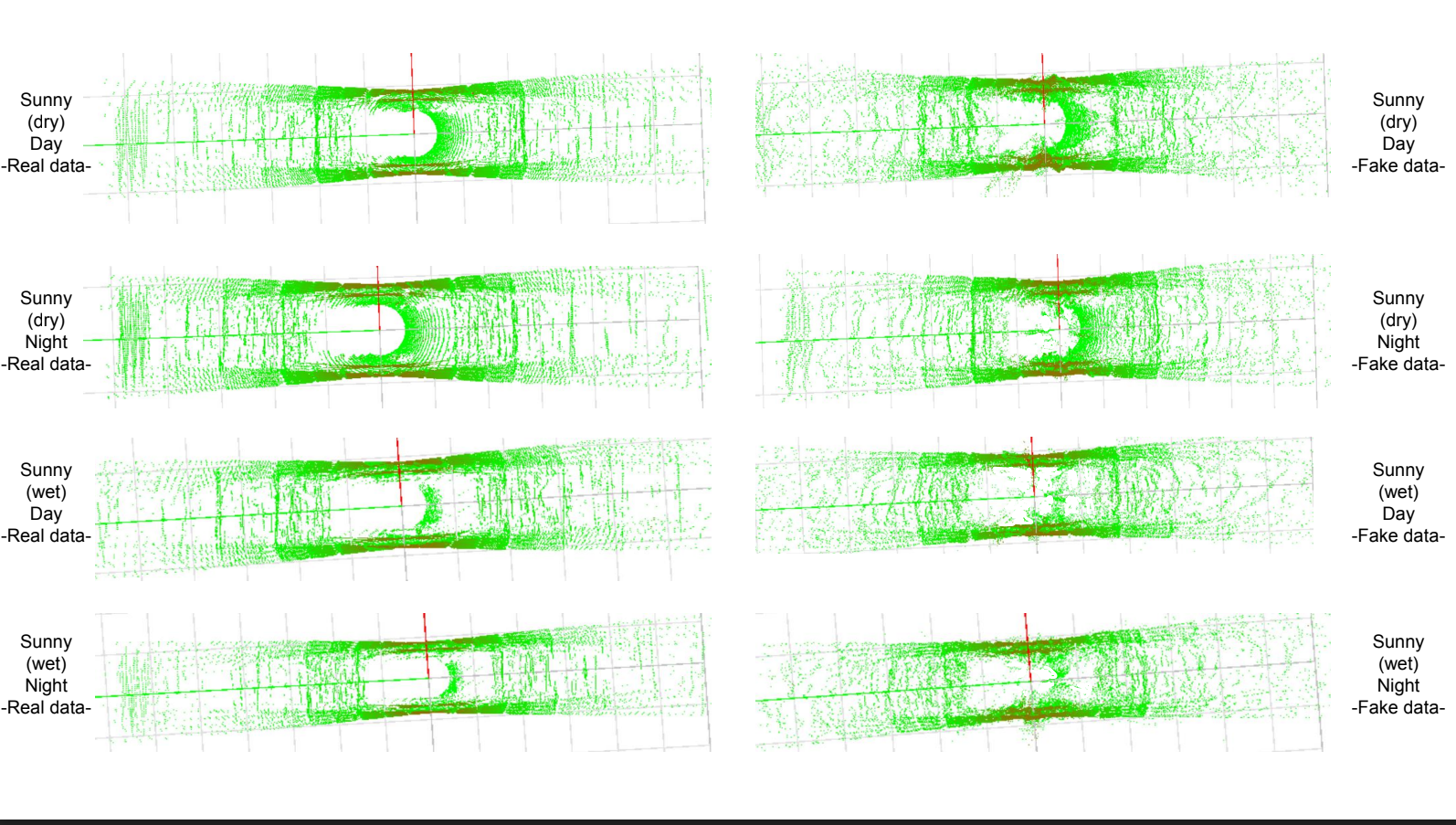
画像だけでなく、自動運転ではよく使われるLiDARセンサに対する雨や霧環境へのスタイル変換モデルを提案しています。
Not only images, but also we proposed style transfer model of LiDAR scans to adverse conditions, such as foggy and rainy conditions, which is a common problem in autonomous driving.

自動運転や先進運転支援システム(ADAS)を考える上で、歩行者/自転車などの交通弱者の安全性の確保は不可欠です。当研究室ではこのテーマに対して、歩行者や自転車の検出から行動認識にわたる様々なレイヤーにアプローチしています。
Ensuring the safety of vulnerable road users such as pedestrians/bicycles is essential for autonomous driving and advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS). In our laboratory, we are focusing on this topic from various layers ranging from pedestrian and bicycle detection to action recognition.
弱教師あり分類機を用いて、3段階の危険度に応じて交通シーンを分類するEnd-to-Endモデルを提案しています。
Using a weakly supervised classifier, we propose an End-to-End model that classifies traffic scenes according to three risk levels.
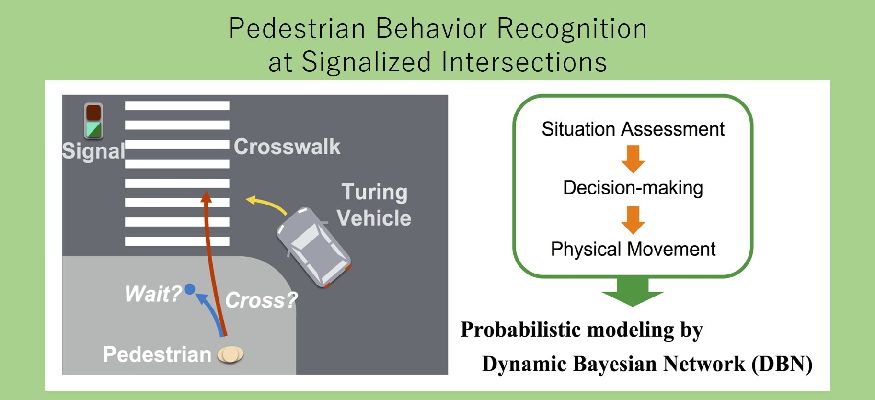
信号交差点シーンにおける様々なコンテキストを考慮したモデルによって、急に駆け込みや停止し得る歩行者行動の認識/予測を行います。
Through a model taking in consideration the various scenes of a signal intersection, we estimate the movement of a pedestrian who might dash or stop suddenly at the intersection.
都市の交差点での交通状況を空間的および時間的に分析するためのステレオビジョンおよび3Dデジタルマップベースのアプローチを提案します。
We propose an approach of using stereo vision and digital 3D map as a basis to analyze the traffic situation at an urban intersection in both space and time dimensions.
自動運転において、急激な減加速は乗客の快適さや周辺車両への影響などを考えると適切ではありません。そのため周囲の交通状況を認識し人間のドライバーと同じような行動計画を提案します。
In autonomous driving, sudden deceleration is not good in terms of passenger comfort and effect on nearby vehicles. To deal with this, we propose a more human-like motion planning which takes into consideration the traffic situation and environment around the vehicle.

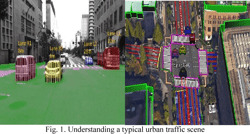
自動運転において、交差点での周囲の状況の認識とそれに基づいた自車両の行動計画は重要な課題の一つです。当研究室では、都市の複雑な交差点での状況認識と行動計画を研究しています。
In autonomous driving, understanding the situation at an intersection and the vehicle reacting to it accordingly (motion planning) is an important task. At our laboratory, we research the scene recognition and motion planning in a complex urban intersection.
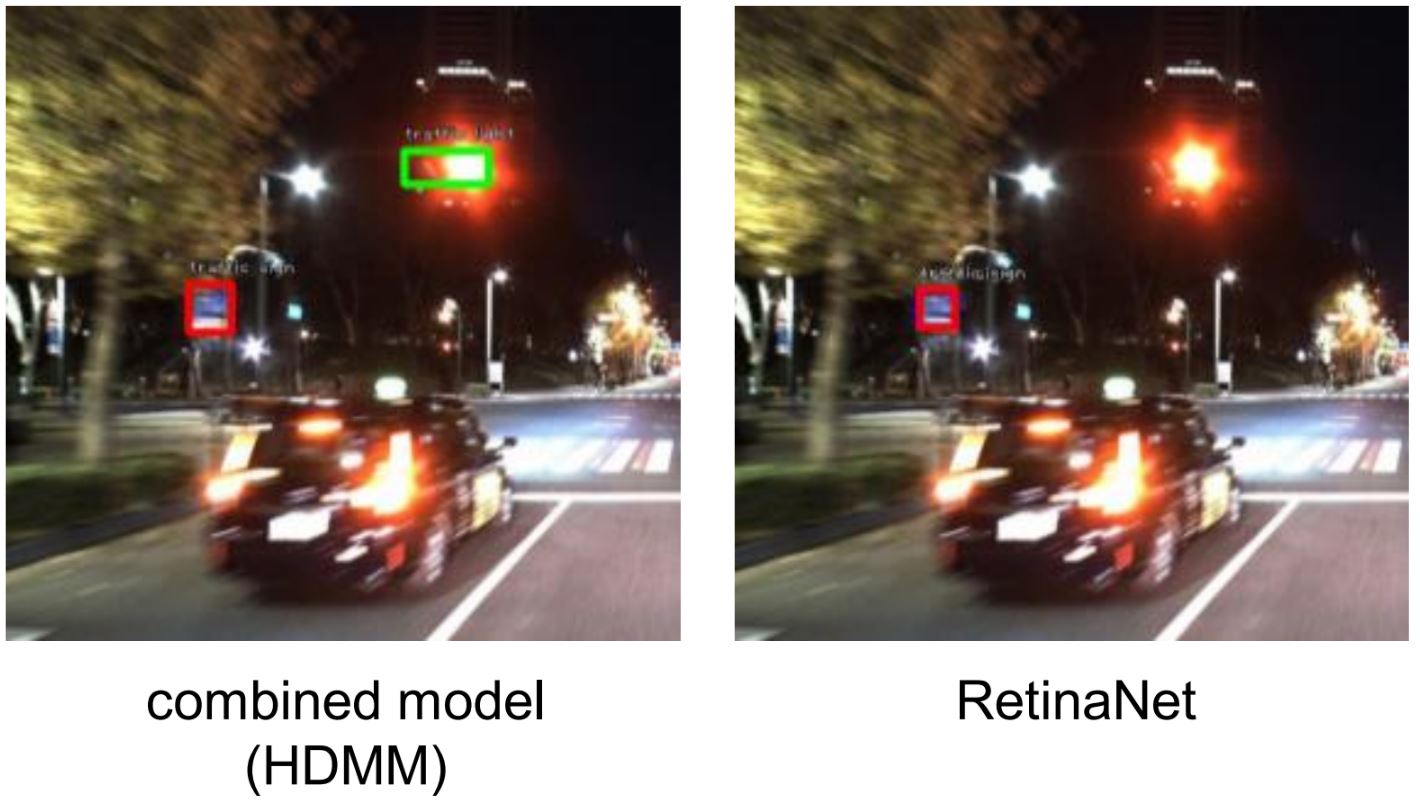
High definition (HD) 地図は環境に対する様々な情報を提供する、自動運転のためのデータソースです。本研究では、HD地図を用いた深層学習ベースのobject detectionモデルの提案を行っています。HD地図から得られる物体の位置情報と画像データを組み合わせることで、特に悪環境におけるobject detectionにおいて高精度の結果を達成しています。
High definition (HD) maps are a data source for autonomus driving that provides a variety of information about the environment. In this study, we propose a deep learning-based object detection model using HD maps. By combining the object location information from HD maps with image data, we have achieved highly accurate results in object detection, especially in adverse environments.
既存のドライブレコーダは、高価で、また不必要にデータを保存してしまう問題を抱えています。本研究ではスマートフォンを用いた車両速度推定や周辺物体認識によって、運転補助に必要な情報を提供する安価なドライブレコーダを提案します。
Existing drive recorders are expensive and have the problem of storing data unnecessarily. This research proposes an inexpensive drive recorder that provides necessary information for driving assistance by estimating vehicle speed and recognizing surrounding objects using a smartphone.
時空間MRFモデルを用いた前景物体抽出とHOG特徴量などを用いた物体識別アルゴリズムを組み合わせ、車載カメラ映像から歩行者のみの検出を行います。
Combining Space-time MRF model (ST-MRF) foreground object detection and HOG feature value algorithms, we conduct the detection of pedestrians only from an onboard vehicle camera feed.
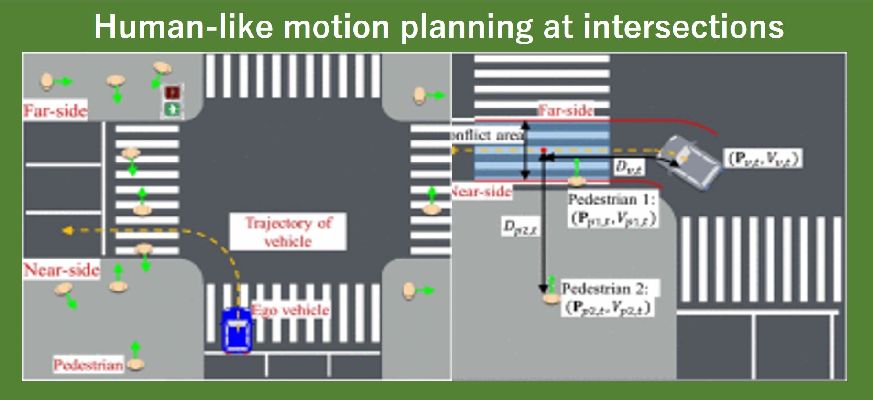
歩行者と自転車を識別した上で、HOG特徴量やSVM、拘束条件を用いて、注意/進行方向を表す頭部や胴部姿勢を推定します。
Recognition and Pose Estimation of Urban Road Users from On-board Cameras
歩車間通信における電波強度(RSSI)を元に、車両に対する歩行者の相対位置を推定します。
Using received signal strength indication (RSSI) as a base, we estimate the relative position of a pedestrian with regards to a vehicle.
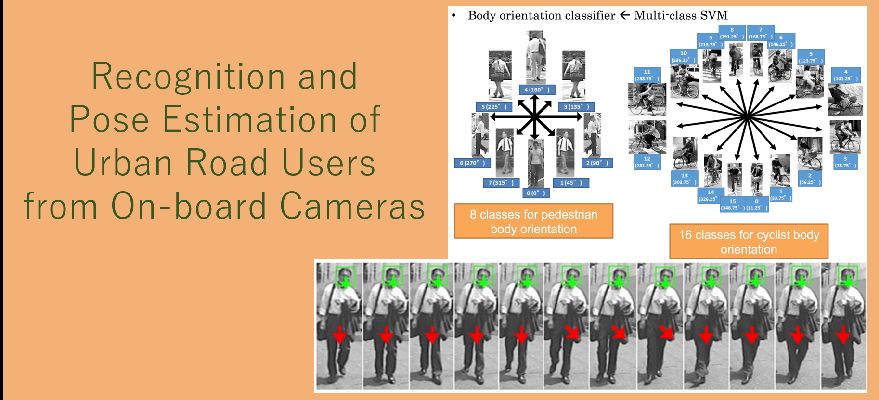
スマートフォンに標準的に搭載されている加速度センサや磁気センサを用い、歩行動作(歩幅、進行方向)を検出し、加算的に歩行者の相対位置推定(歩行者デッドレコニングを行います。さらに、GPSとの融合により、高精度な自己位置推定を行います。
Using acceleration sensor and magnetic sensor commonly found in smartphones, we detect pedestrian movement (step width, direction) and additively calculate their relative position (pedestrian dead reckoning). In addition, by fusing the data with GPS we can accurately measure their location.


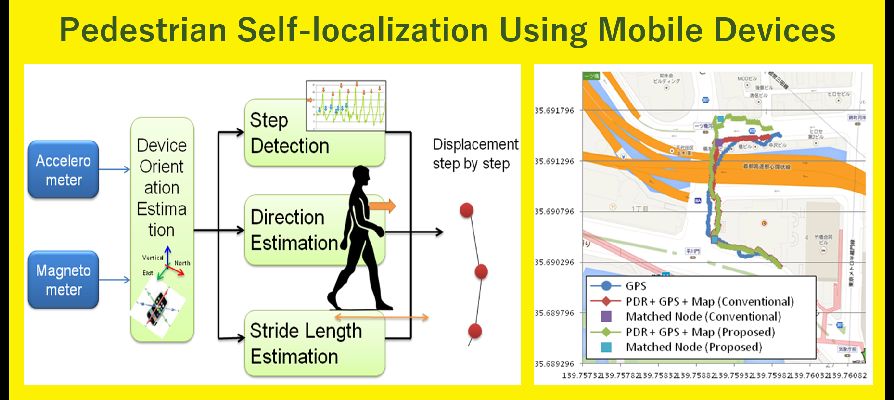
自動運転や高度交通システム(ITS)やスマートフォンアプリケーションにおいて、自己の位置を正確に知ることは非常に重要です。 このテーマでは、特に都市部における自己位置推定に焦点を当て、 GPSをはじめとするGNSS(衛星測位システム: Global Navigation Satellite System)や慣性センサなど車載/モバイル端末センサなどを用いて、 高精度な位置推定が可能な手法の確立を目指しています。
For autonomous driving vehicles, Intelligent Transport Systems (ITS) and smartphone applications, it is important to determine one's location accurately. Under this theme, we are aiming to establish methods to determine location precisely using such technologies as GPS, GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System), inertia sensor mounted in a car, mobile device sensors among others. Focus is placed especially on localization in urban environments.
実環境下で合成的に生成した障害物とのオクルージョンの影響を比較することで,都市部(新宿)において安定した自己位置推定を行うための,HDマップの必要性を示します.
By comparing the effect of occlusion with synthetically generated obstacles in a real environment, we show the necessity of HD maps for stable self-localization in an urban area (Shinjuku).
GISで提供される地形データとしてのVector地図と、自己位置推定に用いられるHD地図は別々に管理されてきました。本研究では、それらを統合的に扱うことのできる地図を提案します。
Vector maps as topographic data provided by GIS and HD maps used for self-location estimation have been managed separately. In this study, we propose an integrated map that can handle them.
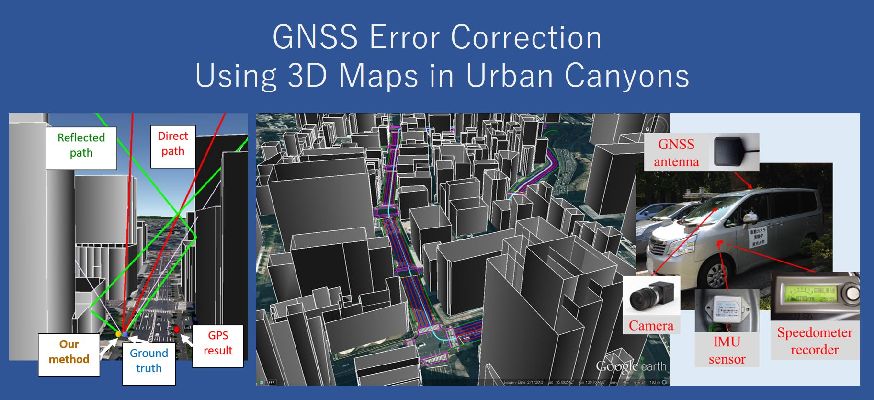
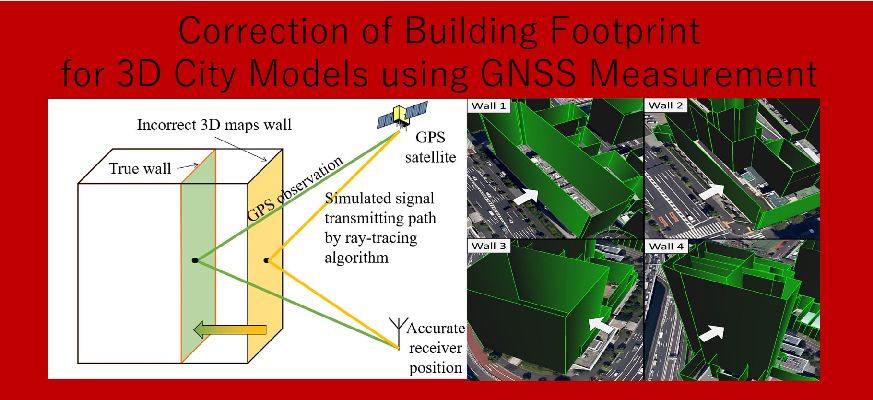
都市部においてGNSSの主要な誤差となっているマルチパスとNLOS伝搬遅延を3次元地図とレイトレーシング法を用いて補正します。さらに、Multi-GNSSやL1-SAIF信号情報なども用いてより高精度な位置推定を行います。
Using 3D maps and ray tracing, we corrected multipass and NLOS propagation delay, which are the main cause for GNSS error in urban environments. In addition, we could determine the location more accurately using Multi-GNSS and L1-SAIF signal information among others.
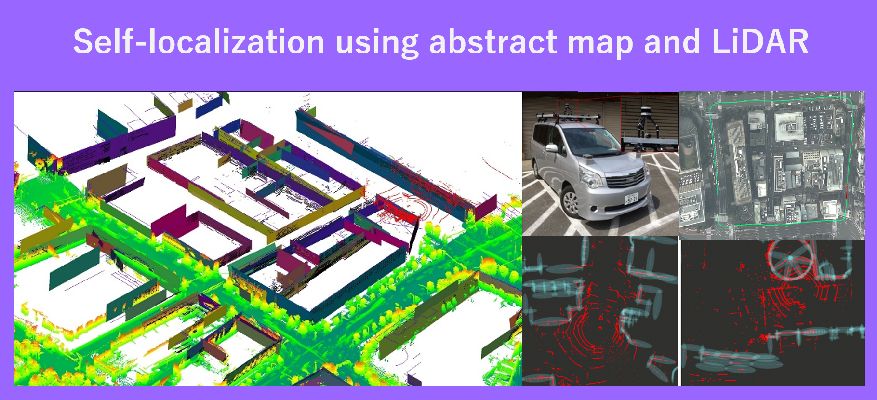
都市部においてGNSSを用いた自己位置推定は十分な精度を達成できません。最先端の自己位置推定手法として3D地図とLiDARのマッチングによるものがありますが、3D地図の作成は容易ではありません。そのため2D地図とLiDARによる自己位置推定を行います。
Self-localization using GNSS in urban environments is not accurate enough in most cases. State-of-the-art self-localization includes methods such as matching 3D map and LiDAR data, but creating 3D maps is not a simple process. Instead, we used 2D maps and LiDAR as a method for self-localization.
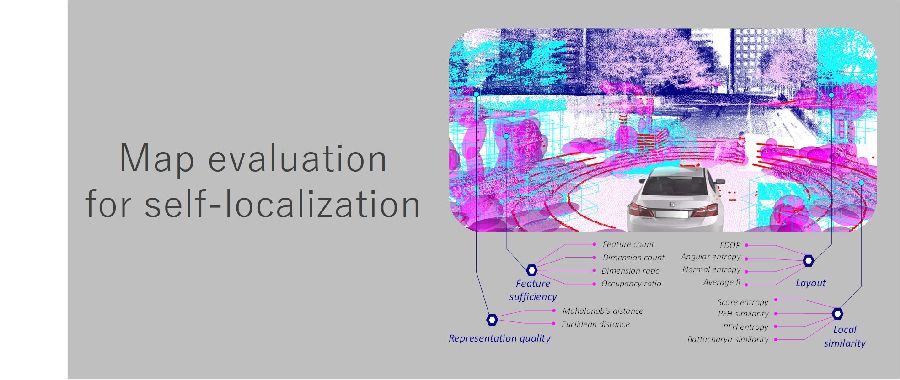
LiDARとマップのマッチングは自己位置推定において注目が集まる技術です。本研究では、自己位置推定の誤差の要因としてマップに焦点を当て様々なシナリオで全く新しいマップの評価を行いました。
Matching LiDAR and map data for the purpose of self-localization is a technology which has gathered attention in the research community. In this research we focused on map, which is the main cause for self-localization error, and conducted a completely novel evaluation of a map in various situations.
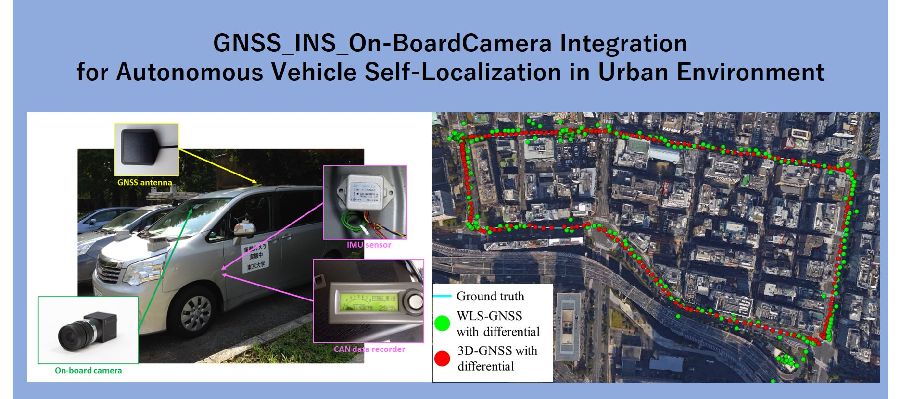
車速センサやジャイロセンサなどをGNSS測位と融合させ、より高精度な車両の自己位置推定を行います。
Fusing vehicle speed sensor and gyro sensor etc. with GNSS positioning, we achieve more precise self-localization of a vehicle.
3次元地図はカメラやレーザーシステムを用いた自己位置推定法や当研究室の高精度なGNSS測位法において必要不可欠であり、3次元地図の精度は自己位置推定結果に大きな影響を与えます。このテーマでは、3次元地図の生成や修正方法について研究しています。
A 3D map is essential for self-localization using cameras and laser systems, in addition to our high accuracy GNSS positioning method. The accuracy of a 3D map greatly affects the result of self-localization, and under this theme, we research methods on creating and improving 3D maps.
MMSによって収集される巨大な3次元点群データから建物の2次元境界を抽出し、よりシンプルかつ必要十分な情報を含む3次元地図を生成する手法について研究しています。
From a big 3D point cloud collected by MMS, we extract 2D borders of a building while conducting research on methods to create simpler but still detailed enough 3D maps.
3次元地図に含まれる建物の2次元境界の位置の誤差を、当研究室のGNSS測位法を用いて修正する手法について研究しています。
Using our GNSS positioning, we research a method to correct location error of a building in a 3D map.

人の位置推定や行動認識にはGPSや監視カメラを用いた技術が広く使われています。 しかし、GPSはショッピングモールのような大規模な屋内環境では精度が低下し、監視カメラを屋内環境全てに設置することはコスト高という問題があります。 そのため、スマートフォンセンサーを用いた屋内での位置推定やその分析による行動推定を行います。
Technologies using GPS and surveillance cameras are widely used for human location estimation and behavior recognition. However, GPS is less accurate in large indoor environments such as shopping malls, and installing surveillance cameras in all indoor environments is costly. Therefore, we use smartphone sensors for indoor location estimation and its analysis for behavior estimation.
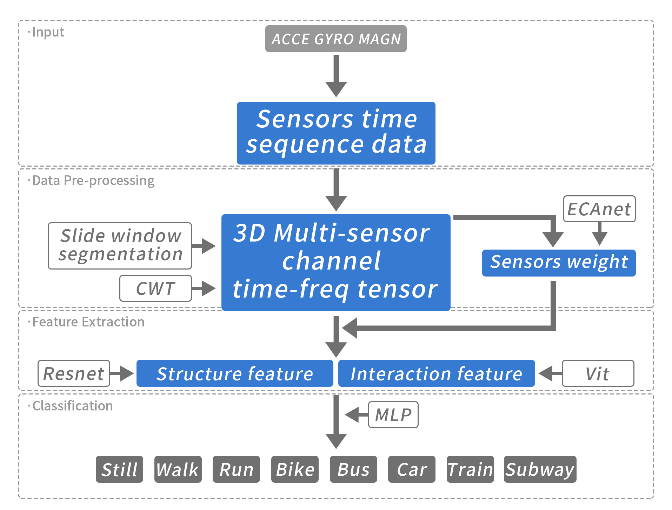
Transportation Mode Detection (TMD)は、ユーザの移動手段をデバイスのセンサ情報から推定するタスクです。スマートフォンのセンサーを利用したTMDは、特に低コストですが、その性能は応用に耐えうるものではありません。本研究では、構造特徴と空間的相互作用特徴を組み合わせるViT (Vision Transformer)を使う、新しいネットワークフレームワークを提案します。
Transportation Mode Detection (TMD) is the task of estimating a user's mode of travel from the device's sensor information. TMD using smartphone seasors is particularly low-cost, but its performance is not application-proven. We propose a novel network framework that uses ViT (Vision Transformer), which combines structural features with spatial interaction features.
スマートフォンセンサーのみを用いて人の活動状況の要因となる3つのアクティビティ(座る/立つ/歩く)と6つのモード(スイング/ハンドリング/コーリング/ポケット/ハンドバッグ/バックパック)を推定します。
Using only smartphone sensors, we estimate human behaviour based on three main activities (sit/stand/walk) and six types of modes (swinging/handling/calling/inside a pocket/inside a handbag/inside a backpack).
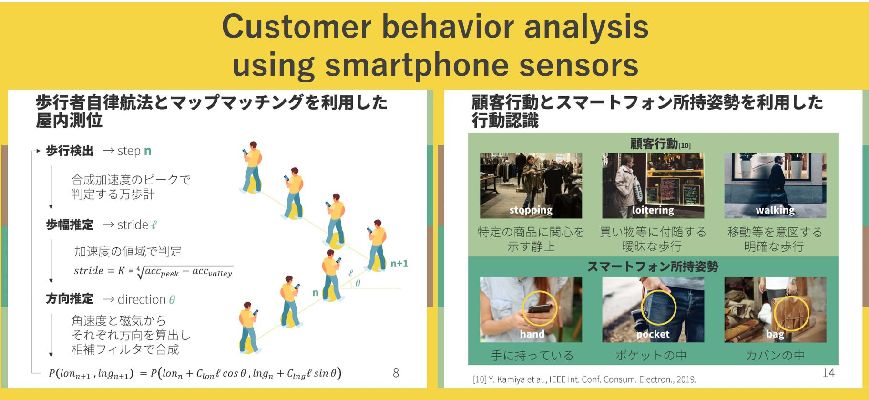
スマートフォンの内蔵センサーを利用して、コンテキストベースのマップマッチングとアクティビティ認識を組み合わせた顧客コンテキスト分析システムを提案します。
Using sensors inside a smartphone, we propose a system which analyses customer context based on a combination of context-based map matching and activity recognition.
GPSによる位置推定はショッピングモールなど屋内環境では精度が低下します。そこでスマートフォンを用いて大規模な屋内環境において、コンテキストベースのマップマッチングを備えた正確な屋内測位システムを提案します。
GPS based localization loses accuracy in indoor environments such as shopping malls. To address this, we propose an accurate indoor localization system using context-based map matching and smartphone sensors inside a large-scale indoor environment.
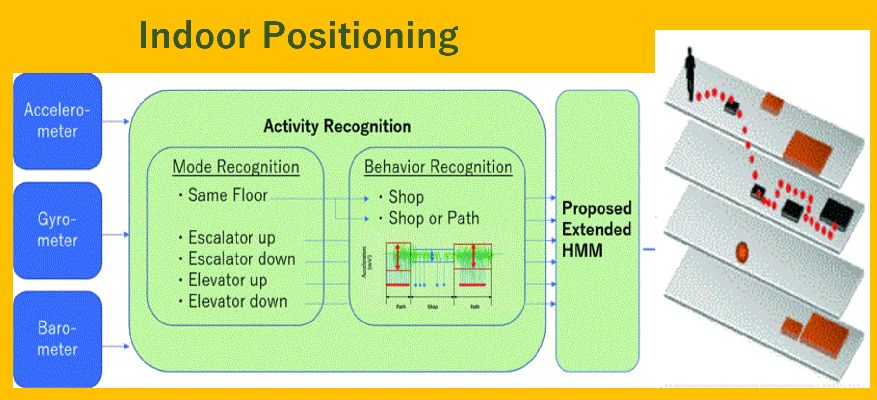
スマートフォンは私たちがどこに行き、どこに滞在するか記録することができます。しかし、その情報は緯度と経度として記録され直感的に理解することは困難です。当研究室ではそこから、ユーザーの滞在場所やそこでの行動を推定します。
Smartphones have the ability to record where we go and where we are at a given moment. However, the information is recorded in longitudinal and latitudinal coordinates, and is therefore hard to understand intuitively. At our laboratory we use this information to estimate user location and activity.

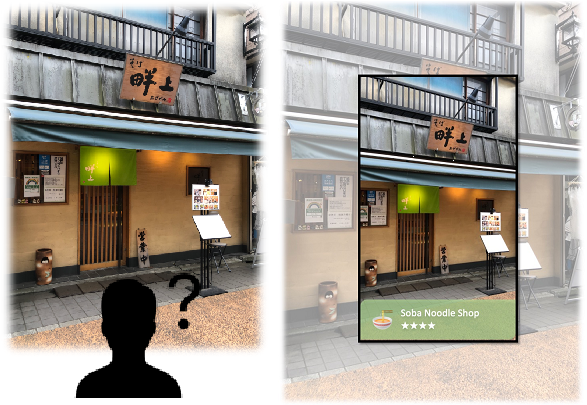
画像内の特徴量とテキスト情報をうまく組み合わせる本研究の画像検索と位置推定技術を提案しています。本研究の技術を用いると、スマートフォンで撮影した画像で自分がどこにいるのか、目の前にある施設は何なのかをデータベースから探索することができるようになります。
We propose an image retrieval and position estimation technique in this research that successfully combines features in images and textual information. Using this research technology, it will be possible to search a database for where you are and what facilities are in front of you in an image taken with a smartphone.
スマートグラスのナビゲーション技術を開発することで、歩行者に新しい体験を提供します。
Using wearable smart glass, we combine our pedestrian localization method and image matching technology to achieve high accuracy localization. Furthermore, we aim to provide a new navigation experience by applying augmented reality (AR) technology to localization.


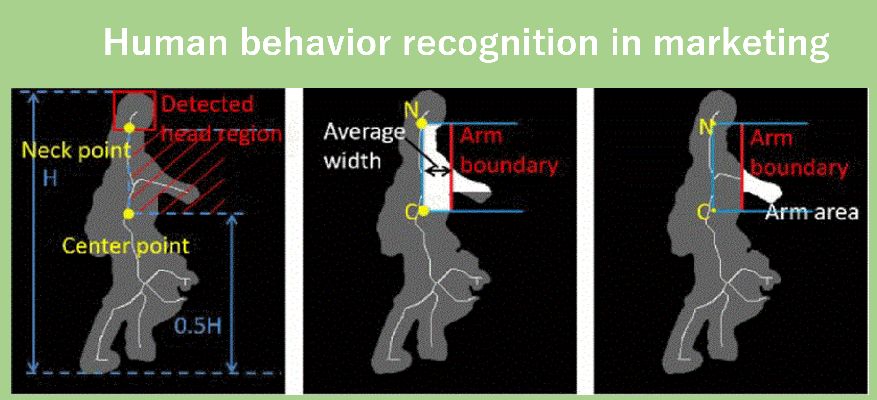
マーケティングにおいて、購買者の商品への興味を推定することは重要です。 購買者の興味の推定のために、店内に設置された監視カメラの画像を用いて購買者の行動認識や姿勢推定を行っています。
In marketing, it is important to estimate the interest level of a customer towards a product. To estimate the interest level of a customer, we conduct behaviour recognition and pose estimation of the customer using cameras installed inside the store.
購買者の関心には、購買者の体の向きが大きく関係しています.当研究室では、監視カメラからの向きを考慮した時空間深層ニューラルネットワークを使用した顧客姿勢推定システムを提案しています。
In estimating customer's interest level, their body direction plays an important role. At our laboratory, we propose a system using surveillance camera and space-time deep neural network model to estimate customer's pose.
小売店などに設置されるカメラから顧客の商品に対する関心/行動を推定する手法について研究を行っています。
We conduct research on methods to estimate the interest level towards a product and behaviour recognition of a customer in retail shops using cameras.
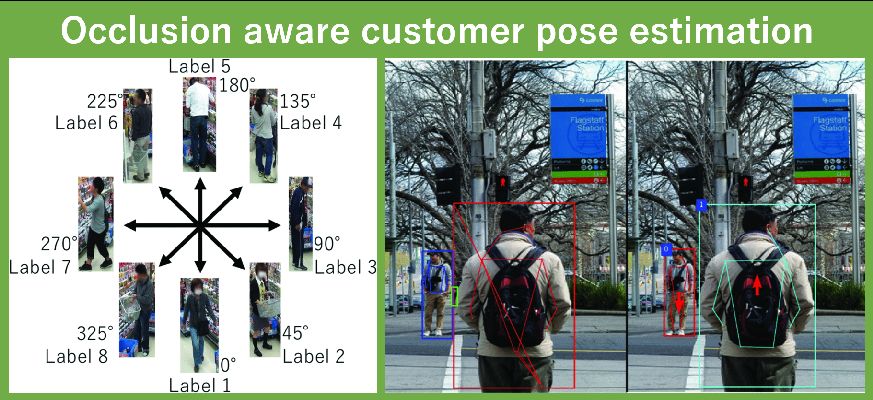
姿勢推定に多く用いられる関節推定は、オクルージョン状態では正しく推定されないことがあります。そこで、マスク領域ベースの畳み込みニューラルネットワーク(Mask R-CNN)による複数人の姿勢推定を提案しています。
Joint estimation often used in pose estimation is not usually accurate in case of an occlusion. Therefore we propose a multiple people pose estimation method using Mask Region based Convolutional Neural Network (Mask R-CNN).
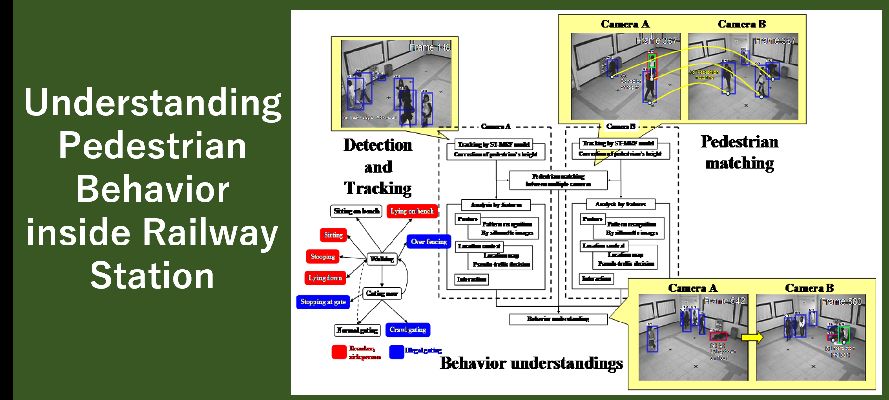
オブジェクトの姿勢情報と位置情報を組み合わせることで駅構内における人物の行動把握フレームワークの構築を行いました。
Combining object pose information with location information, we built a framework for human behaviour recognition inside a railway station.

昼間の交通画像を夜間の画像へ変換するために、Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) による画像生成とSemantic Segmentationを組み合わせたモデルを提案します。
We proposed a generative model to use semantic segmentation networks in GANs for the day-to-night image style transfer.
画像だけでなく、自動運転ではよく使われるLiDARセンサに対する雨や霧環境へのスタイル変換モデルを提案しています。
Not only images, but also we proposed style transfer model of LiDAR scans to adverse conditions, such as foggy and rainy conditions, which is a common problem in autonomous driving.
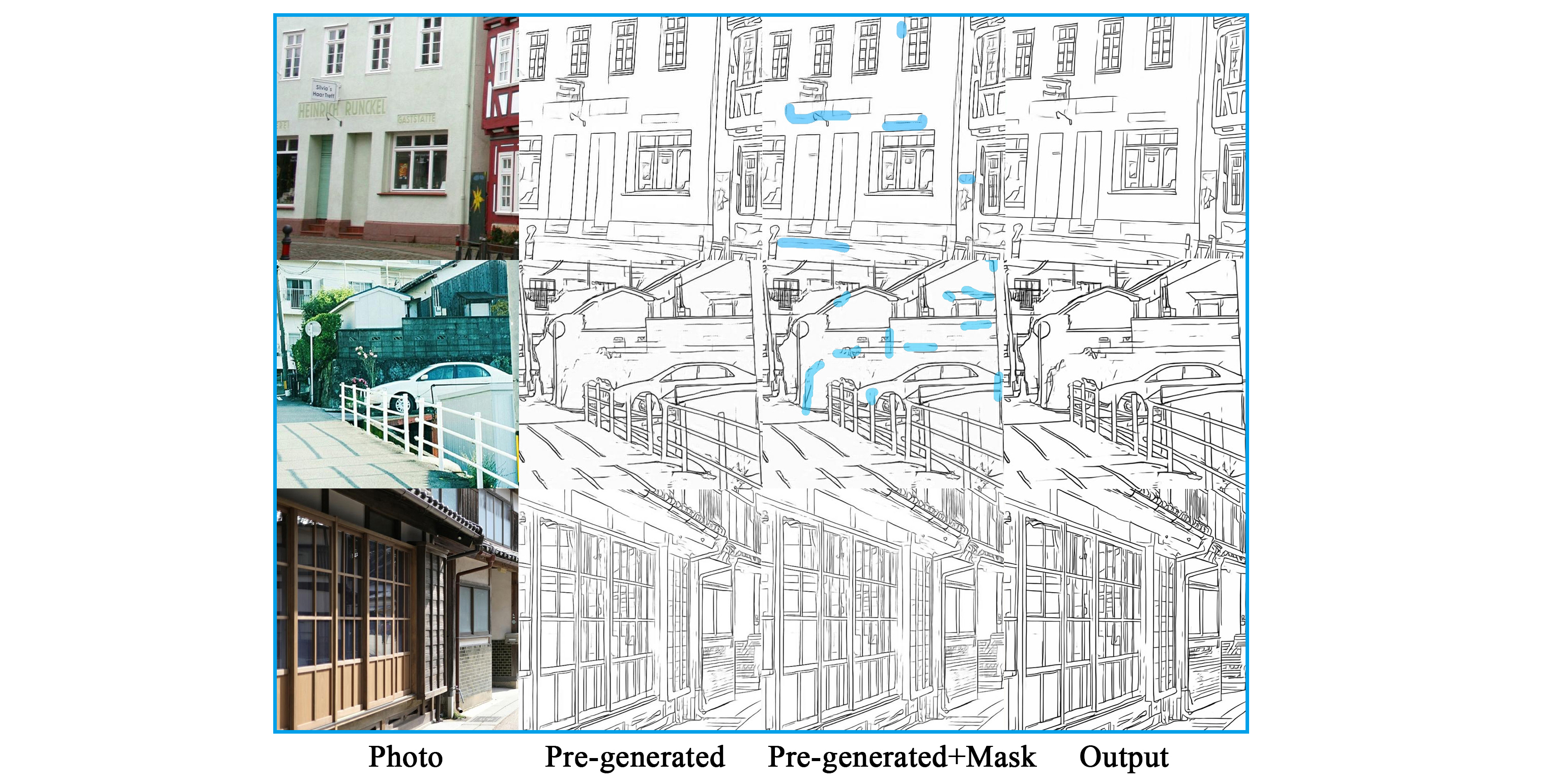
漫画の背景に写実的な要素を加えたいニーズがありますが、写真には不要な要素が写り込んでいる場合があります。本研究では、セレクションペンとスマートブラシを使用してマスクを生成し、写真から不要な要素を除去した線画の最適化を実現します。
There is a need to add photorealistic elements to the background of a Manga, but unwanted elements may be present in the photo. This study uses selection pens and smart brushes to generate masks to optimize line drawings that remove unwanted elements from photographs.
画像生成のための条件付きGANs(CGANs)における不均衡データセットの課題に取り組んでいます。リサンプリングと微分可能な拡張を組み合わせたベースラインモデルに加え、スタイルに依存する特徴とスタイルに依存しない特徴を分離して扱う新しいCGANs (SandGAN) を提案します。
We address the challenge of unbalanced datasets in conditional GANs (CGANs) for image generation. In addition to a baseline model that combines resampling and differentiable extensions, we propose new CGANs (SandGANs) that treat style-dependent and style-independent features separately.
本研究では、新しい標本の生成方法を学習するだけでなく潜在変数と出力画像との対応関係を決定する、潜在的空間を理解可能なネットワークSelf-excited Generative Adversarial Network(SelfExGAN)を提案しています。
We propose latent space understanding Self-excited Generative Adversarial Network(SelfExGAN), which is capable of not only learning to create new samples but also to understand the relationship between latent vector and generated image.


Transportation Mode Detection (TMD)は、ITSやライフログにとって重要な課題です。スマートフォンのセンサーを利用したTMDは、特に低コストですが、その性能は応用に耐えうるものではありません。本研究では、構造特徴と空間的相互作用特徴を組み合わせるViT (Vision Transformer)を使う、新しいネットワークフレームワークを提案します。
Transportation Mode Detection (TMD) is the task of estimating a user's mode of travel from the device's sensor information. TMD using smartphone seasors is particularly low-cost, but its performance is not application-proven. We propose a novel network framework that uses ViT (Vision Transformer), which combines structural features with spatial interaction features.
画像内の特徴量とテキスト情報をうまく組み合わせる本研究の画像検索と位置推定技術を提案しています。本研究の技術を用いると、スマートフォンで撮影した画像で自分がどこにいるのか、目の前にある施設は何なのかをデータベースから探索することができるようになります。
We propose an image retrieval and position estimation technique in this research that successfully combines features in images and textual information. Using this research technology, it will be possible to search a database for where you are and what facilities are in front of you in an image taken with a smartphone.
High definition (HD) 地図は環境に対する様々な情報を提供する、自動運転のためのデータソースです。本研究では、HD地図を用いた深層学習ベースのobject detectionモデルの提案を行っています。HD地図から得られる物体の位置情報と画像データを組み合わせることで、特に悪環境におけるobject detectionにおいて高精度の結果を達成しています。
High definition (HD) maps are a data source for autonomus driving that provides a variety of information about the environment. In this study, we propose a deep learning-based object detection model using HD maps. By combining the object location information from HD maps with image data, we have achieved highly accurate results in object detection, especially in adverse environments.
弱教師あり分類機を用いて、3段階の危険度に応じて交通シーンを分類するEnd-to-Endモデルを提案しています。
Using a weakly supervised classifier, we propose an End-to-End model that classifies traffic scenes according to three risk levels.




Neural Architecture Search (NAS) は、タスクに対してニューラルネットワークの構造(活性化関数やコネクション)の探索を行うタスクです。
Neural Architecture Search (NAS) is a task that searches for neural network structures (activation functions and connections) for a task.
本研究では、TrueSkillを用いたランキングアルゴリズムと、Neural Networksを学習なしで評価する指標を組み合わせることで効率的なNASの実現を目指します。
This research aims to realize an efficient NAS by combining a ranking algorithm using TrueSkill and a metric to evaluate Neural Networks without training.
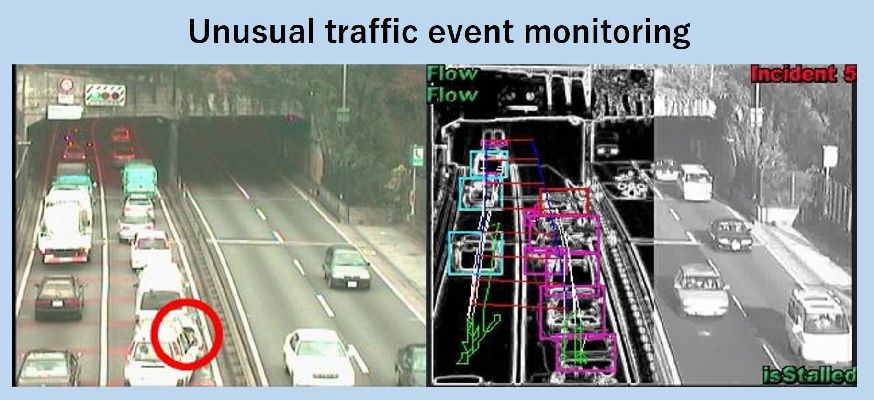
近年、道路交通環境にも多くの監視カメラが設置され、交通流の計測や事故等の交通事象の検出が行われています。当研究室では、人の手作業に頼らずこうした監視カメラ画像から自動的に意図する情報を抽出する技術の研究を行ってきました。
In recent years, surveillance cameras have been installed in road environments for example to measure the amount of traffic and to detect traffic accidents. At our laboratory, we conducted research about technology which automatically extracts relevant information from surveillance camera feed without the need for human intervention.
オクルージョンにも屈強なトラッキング手法を用い、方向別統計量・平均速度・交通密度などの交通事象に関する統計量を自動的に取得するシステムを開発しました。
Using occlusion-robust tracking techniques, we developed a system which automatically obtains direction, average speed, traffic intensity and other traffic relevant statistics.
交通流監視において、カメラ映像入力と画像処理技術の活用により、事故、渋滞、停止車両、落下物のような交通事象をリアルタイムに検出するシステムを構築しました。
In the field of traffic flow monitoring, we built a system which detects accidents, traffic congestion, stopped vehicles, fallen objects and other such traffic related phenomenons in real-time using video from a camera as an input and applying image processing techniques.

従来の交通信号制御は、サイクル長やスプリットといったパラメータが定められており、交通閑散時も赤信号によって不必要な待ち時間が発生するという問題がありました。これに対し、当研究室では路車協調型の交差点制御方法を研究してきました。
Previous traffic signal control had fixed cycle length and split parameter values, which caused problems such as unnecessary waiting time due to red lights even when there was virtually no traffic. In this regards, we conducted research regarding a cooperative-type intersection control method.
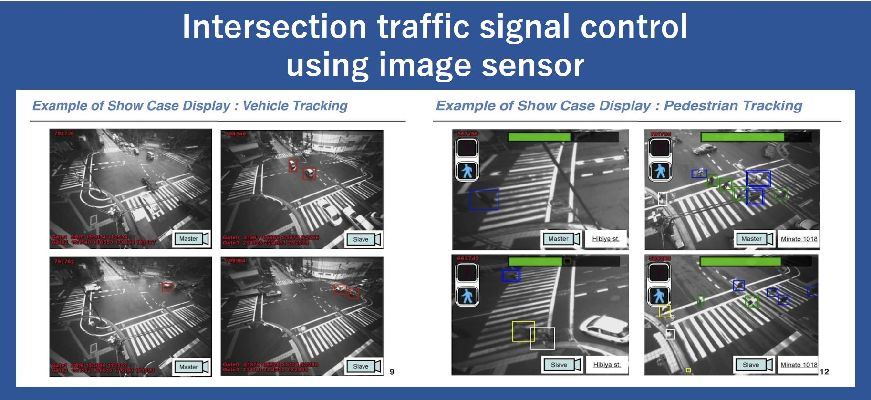
車両と歩行者の計測機能を集約した先進的な画像センサが、車両用/歩行者用信号スプリットを最適化に有用であることを提案しました。
We proposed that an advanced image sensor, which measures both vehicles and pedestrians, is helpful in the optimization of traffic signal split for vehicles and pedestrians.